Cosc101 keypoints
computer can be defined as an electronic device that takes data as input from the user, processes the data under control of set of instructions (called program),stores the data and generates result as output in a required format.
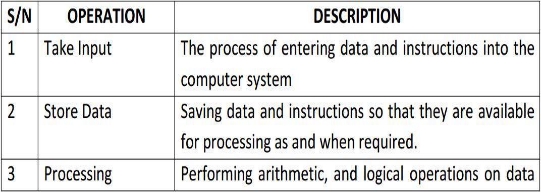
Any digital computer carries out five functions as follows:
- Takes data as input.
- Stores the data/instructions in its memory and use them when required.
- Processes the data and converts it into useful information.
- Generates the output
- Controls all the above four steps.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS High Speed
Computer has units of speed in microsecond, nanosecond, and even the
picoseconds. Accuracy
In addition to being very fast, computers are very accurate. Storage
A computer has much more storage capacity than human beings. It can store
large amount of data such as images, videos, text, audio and many others. Diligence
Unlike human beings, a computer is free from monotony, tiredness and lack of
concentration. Versatility
A computer is very flexible in performing the jobs and can be used to solve
problems related to various fields. Automation
Automation means ability to perform the given task automatically. BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS
Trying to use machines to solve mathematical problems can be traced to the early
17th century. Wilhelm Schickhard, Blaise Pascal, and Gottfried Leibnitz were
among mathematicians who designed and implemented calculators that were
capable of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The first multipurpose or programmable
computing device was probably Charles Babbage's
Difference Engine, which was begun in 1823 but never completed. In 1842,
Babbage designed a more ambitious machine, called the Analytical Engine but
unfortunately it was also only partially completed. EVOLUTION AND GENERATIONS OF COMPUTERS First Generation Computers
The period of first generation was 1945-1959. The computers of first generation
used vacuum tubes as the basic components for memory and circuitry for CPU
Central Processing Unit. Characteristics of First Generation Computers
- Used vacuum tube technology
- Supported machine language only
- Generated lot of heat
- Slow input and output devices
- Huge size
- Non-portable
- Consumed lot of electricity
Some computers of this generation were: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701, IBM-
\650. Second Generation Computers
The period of second generation was 1959-1965. In this generation transistors
were used that were cheaper, consumed less power, more compact in size, more
reliable and faster than the first generation machines made of vacuum tubes.** The main features of second generation computers are:
- Use of transistors
- Reliable in comparison to first generation computers
- Smaller size as compared to first generation computers
- Generated less heat as compared to first generation computers
- Consumed less electricity as compared to first generation computers
- Faster than first generation computers
- Supported machine and assembly languages
Some computers of this generation were: IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC
3600, UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers
The period of third generation was 1965-1975. The computers of third generation
used integrated circuits IC′s in place of transistors. A single IC has many transistors,
resistors and capacitors along with the associated circuitry. The main features of third generation are:
Used IC
More reliable in comparison to previous two generations Ø Smaller size
- Generated less heat
- Faster
- Lesser maintenance
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Supported high-level language
Some computers of this generation were: IBM-360 series, Honeywell-6000 series,
PDP (Personal Data Processor), IBM-370/168, TDC-316 Fourth Generation Computers
The period of fourth generation was 1975-1985. The computers of fourth
generation used Very Large Scale Integrated VLSI circuits. VLSI circuits having
about 5000 transistors and other circuit elements and their associated circuits on
a single chip made it possible to have microcomputers of fourth generation. The main features of fourth generation are:
- VLSI technology used
- Very cheap
- Portable and reliable
- Use of PC's
- Very small size
- Pipeline processing
- Concept of internet was introduced
- Great developments in the fields of networks
Some computers of this generation were: DEC 10, STAR 1000, PDP 11, CRAY-Super
Computer, CRAY-X-MP Super Computer.
Fifth Generation Computers
The period of fifth generation is 1985-till date. In the fifth generation, the VLSI technology became ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology, resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million electronic components.
This generation is based on parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial
Intelligence) software. The main features of fifth generation are:
- ULSI technology in use
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Development of Natural language processing
- Advancement in Parallel Processing
- Advancement in Superconductor technology
- More user friendly interfaces with multimedia features
- Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates
Some computer types of this generation are: Desktop, Laptop, NoteBook,
UltraBook, ChromeBook, TYPES OF COMPUTERS PC Personal Computer
A PC can be defined as a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an
individual user. PCs are based on the microprocessor technology that enables
manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Notebook Computer
This is simply a compact form of personal computer. E.g laptop. Notebook
computers have advantage of portability Workstation
Workstation is a computer used for engineering applications CAD/CAM, desktop
publishing, software development, and other such types of applications which
require a moderate amount of computing power and relatively high quality
graphics capabilities. Server System
This is a computer that supports large volumes of data which frequently need to
be accessed or to be modified. It also supports request response operation.
Handheld Computers
This is also called a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant). A computer that fits into a
pocket, runs on batteries, and is used while holding the unit in your hand. Minicomputer
It is a midsize multi-processing system capable of supporting up to 250 users
simultaneously. Mainframe
Mainframe is very large in size and is an expensive computer capable of
supporting hundreds or even thousands of users simultaneously. Supercomputer
Supercomputers are one of the fastest computers currently available.
Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications
that require immense amount of mathematical calculations. For example,
weather forecasting, scientific simulations, animated graphics, fluid dynamic
calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and analysis of geological
data e. g. in petrochemical prospecting. CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS BY THEIR BASIC OPERATING PRINCIPLE Analog Computer
An analog computer (spelt analogue in British English) is a form of computer that
uses continuous physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic
quantities to model the problem being solved.
Examples of analog computers are:
- Thermometer
- Petrol Pump Indicator
- Speedometer
- Multimeter Digital Computer
Most computers today are digital. They represent information discretely and use
a binary system that represents each piece of information as a series of zeroes
and ones. Hybrid Computer (Analog + Digital)
A combination of computer capable of inputting and outputting in both digital
and analog signals. Example HYDAC 2400, Gas pump
station Computer Organization
It refers to the operational units and their interconnection that realize the
architectural specifications. It is concern with the way the hardware components
operate and the way they are connected together to form the computer system.
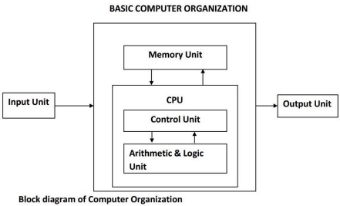

INPUT DEVICE This unit contains devices with the help of which we enter data into computer.
This unit makes link between user and computer.
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is considered as the brain of the computer. CPU performs all types of data
processing operations. It stores data, intermediate results and instructions
(program). It controls the operation of all parts of computer. CPU itself has
following components
- Control Unit
- ALU (Arithmetic & Logic Unit)
Memory Unit or Storage
This unit can store instructions, data and intermediate results. This unit supplies
information to the other units of the computer when needed. Functions of memory unit include:
- Stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
- Stores intermediate results of processing.
- Stores final results of processing before these results are released to an
output device.
All inputs and outputs are transmitted through main memory.
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of computer but does not carry out
any actual data processing operations. Functions of this unit are:
- It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among
other units of a computer.
- It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
- It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs
the operation of the computer.
- It communicates with Input/output devices for transfer of data or results
from storage.
ALU (Arithmetic & Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely Arithmetic section and Logic Section.
Arithmetic Section: Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic
operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. All complex
operations are done by making repetitive use of above operations.
Logic Section: Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as
comparing, selecting, matching and merging of data.
Output Unit
Output unit consists of devices with the help of which we get the information
from computer. This unit is a link between computer and users.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER HARDWARE
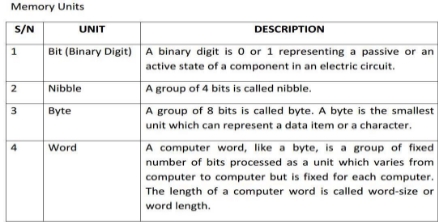
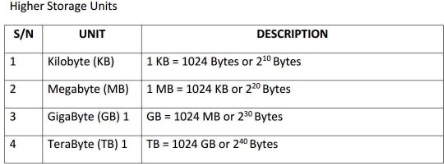
COMPUTER MEMORY
A computer is not one single device, but a system of devices that all work
together. Like the different instruments in a symphony orchestra, each device in a
computer plays its own part. A typical computer
system consists of the following major components:
- The central processing unit (CPU)
- Main memory
- Secondary storage devices
- Input devices
- Output devices
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
A CPU is brain of a computer. It is responsible for all functions and processes.
The CPU is comprised of three main parts :
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Executes all arithmetic and logical operations.
Arithmetic calculations like as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Logical operation like compare numbers, letters, or special characters
- Control Unit (CU): controls and co-ordinates computer components.
- Read the code for the next instruction to be executed.
- Increment the program counter so it points to the next instruction.
- Read whatever data the instruction requires from cells in memory.
- Provide the necessary data to an ALU or register.
- If the instruction requires an ALU or specialized hardware to complete, instruct
the hardware to perform the requested operation.
Main Memory
A memory is just like a store. It is used to store data and instructions. The memory of computer is broadly categories into two categories:
- Internal or Main Memory (Primary)
- External or Permanent Memory (Secondary)
Internal or Main memory
This is also known as the primary memory. It holds only those data and
instructions on which computer is currently working. It is divided into two
subcategories RAM and ROM.
RAM: Random Access Memories are volatile in nature. As soon as the computer is
switched off, the contents of memory are also lost.
ROM: Read only memories. The storage is permanent, but it is read only memory.
We cannot store new information in ROM. Several types of ROM are available:
PROM: Programmable Read Only Memory; it can be programmed once as per
user requirements.
EPROM: Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory; the contents of the memory
can be erased and store new data into the memory.
EEPROM: Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory; in this type of
memory the contents of a particular location can be changed without affecting
the contents of other location.
External or Permanent Memory
This type of memory is also known as the secondary memory or non-volatile.
Stores data and programs permanently, its retained after the power is turned off
It is slower than main memory. For example:
- Hard drive (HD): A hard disk is part of a unit, often called a "disk drive," "hard
drive," or "hard disk drive," that store and provides relatively quick access to large
amounts of data on an electromagnetically charged surface or set of surfaces.
- Optical Disk: an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disk drive that uses laser light as
part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives
can only read from discs, but recent drives are commonly both readers and
recorders, also called burners or writers.
Input is any data the computer collects from people and from other devices.
Output devices
An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment used to
communicate the results of data processing carried out by an information
processing system (such as a computer) which converts the electronically
generated information into human-readable form.
COMPUTER SOFTWARE
Computer cannot do anything on its own. It is the user who instructs computer;
what to do, how to do and when to do. Software can
be classified mainly into two categories namely System Software and Application Software.
System software
can be defined as sets of programs, responsible for running the computer,
controlling various operations of computer systems and management of
computer resources. Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers, Interpreter, and Assemblers etc
Application Software
Application software is a set of programs, which are written to perform specific
tasks, Application
software can be broadly classified into two types:
1) Generalized packages 1) Customized packages
Generalized Packages
These are user friendly software written to cater to user’s very general needs
such as preparing documents, drawing pictures, database to manage
data/information, preparing presentations, play games etc.Some of
the generalized packages are listed below:
- Word Processing Software (for preparing documents): E.g Word Perfect,
MS-Word, OpenOffice.org Writer
- Spreadsheets (Data Analysis): E.g Lotus Smart suites, MSExcel, OpenOffice.org Calc, Apple Numbers
- Presentations: E.g Presentation Graphics, MS-PowerPoint, OpenOffice.org Impress
- Database Management System: E.g MS-Access, OpenOffice.org Base, MSSQL Server, ORACLE
- Graphics Tools: E.g Paint shop pro, Adobe Photoshop
Customized Packages
These are the applications that are customized (or developed) to meet the
specific requirements of an organization/institution. For Example: Student
information details, Payroll packages, inventory control etc.
INTRODUCTION TO OPERATING SYSTEM
An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between the user and
the computer hardware and controls the execution of all kinds of programs.
The operating system's tasks, in the most general sense, fall into six categories:(functions of os)
- Processor management: allocates the processor (CPU) to a process and
deallocates processor when it is no longer required.
- Memory management: keeps tracks of primary memory i.e. what part of it
is in use by whom, what part is not in use etc. and allocates the memory
when a process or program requests it.
- Device management: keeps track of all devices. This is also called I/O
controller that decides which process gets the device, when, and for how
much time.
- Storage management: allocates and de-allocates the resources and decides
who gets the resources.
- Application interface: Let application programmers use functions of the
computer without having to directly keep track of all the details in the
CPU's operation.
- User interface: brings structure to the interaction between a user and the
computer.
TYPES OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
- Real-time operating system (RTOS) - Real-time operating systems are used to
control machinery, scientific instruments and industrial systems.
- Single-user, single task - As the name implies, this operating system is designed
to manage the computer so that one user can effectively do one thing at a time.
- Single-user, multi-tasking - This is the type of operating system most people use
on their desktop and laptop computers today
- Multi-user - A multi-user operating system allows many different users to take
advantage of the computer's resources simultaneously.
Categorization based on manufacturers
Following are some famous manufacturers of Operating Systems:
- Windows
- Linux OS
- Unix OS
- Mac OS
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER PROGRAM PLANNING.
A computer is a useful tool for solving a great variety of problems. The following are some techniques/tools used in computer program planning:
- Algorithm
- Flowchart
- Pseudo code
- Decision table
ALGORITHM
An algorithm can be defined as a process that performs some finite sequence of
operations in order to solve a given problem.(algorithm is a step by step procedure for solving a given problem)
Characteristics of a Good Algorithm
The following are characteristics of a good algorithm
- There must be no ambiguity in any instruction.
- There should not be uncertainty about which instruction to be executed
next.
- The algorithm must be finite, must terminate after a number of steps.
- Must be general enough to deal with any contingency.
Advantages of algorithm
- It is a step-by-step representation of a solution to a given problem, which is
very easy to understand.
- It provides a definite procedure.
- It is independent of programming language.
- It is easy to debug as every step has its own logical sequence
Disadvantages of algorithm
It is time consuming & cumbersome as an algorithm is developed first which is
then converted into flowchart and into a computer program.
Type of Algorithms
Algorithm has three types of control structures. They are:
- Sequence
- Branching (Selection)
- Loop (Repetition)
These three control structures are sufficient for all purposes.
- The sequence is exemplified by sequence of statements place one after the
other – the one above or before another gets executed first.
- The branch refers to a binary decision based on some condition.
- The loop allows a statement or a sequence of statements to be repeatedly
executed based on some loop condition.
Examples of Algorithm
Example 1: Find the area of a Circle of radius r.
Inputs to the algorithm:
Radius r of the Circle.
Expected output:
Area of the Circle
Algorithm:
Step1: Read\input the Radius r of the Circle
Step2: Area PI*r*r // calculation of area
Step3: Print Area
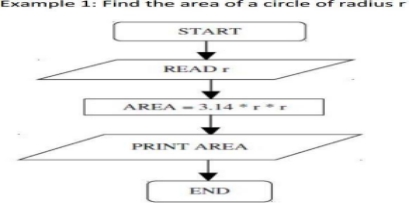
FLOWCHART
A flowchart can therefore be seen as a
type of diagram (graphical or symbolic) that represents an algorithm or process.Flowcharting Symbols
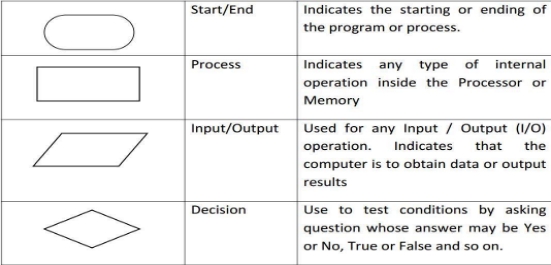
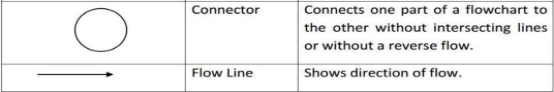
General Rules for flowcharting
- All boxes of the flowchart are connected with Arrows. (Not lines)
- Flowchart symbols have an entry point on the top of the symbol with no other entry points. The exit point for all flowchart symbols is on the bottom except for the Decision symbol.
- The Decision symbol has two exit points; these can be on the sides or the bottom and one side.
- Generally a flowchart will flow from top to bottom. However, an upward flow can be shown as long as it does not exceed 3 symbols.
- Connectors are used to connect breaks in the flowchart. Examples are:
- From one page to another page.
- From the bottom of the page to the top of the same page.
- An upward flow of more than 3 symbols
- All flow charts start with a Terminal or Predefined Process (for interrupt programs or subroutines) symbol.
- All flowcharts end with a terminal or a contentious loop
Advantage of using Flowchart
Some of the benefits of flowcharts are as follows:
1) Communication: Flowcharts are better way of communicating the logic of a
system to all concerned.
2) Effective analysis: With the help of flowchart, problem can be analyzed in more
effective way.
3) Proper documentation: Program flowcharts serve as a good program
documentation, which is needed for various purposes.
4) Efficient Coding: The flowcharts act as a guide or blueprint during the systems
analysis and program development phase.
5) Proper Debugging: The flowchart helps in debugging process. 5) Efficient Program Maintenance: The maintenance of operating program
becomes easy with the help of flowchart.
Limitation of using flowcharts
1) Complex logic: Sometimes, the program logic is quite complicated. In that case,
flowchart becomes complex and clumsy.
2) Alterations and Modifications: If alterations are required the flowchart may
require re-drawing completely.
3) Reproduction: As the flowchart symbols cannot be typed, reproduction of
flowchart becomes a problem.
4) The essentials of what is done can easily be lost in the technical details of how
it is done.
Examples Flowcharts Pseudocode is a generic way of describing an algorithm without use of any specific programming language syntax.
Benefits of Pseudocodes
Pseudocode provides a simple method of developing a program as it uses
everyday language to prepare a brief set of instructions in the order in which they
appear in the completed program.
Language independent
Easier to develop a program from pseudocode than a flowchart
Easy to translate pseudocode into a programming language
Pseudocode is compact and does not tend to run over many pages
Limitations of Pseudo Code
It does not provide visual representation of the program’s logic.
No accepted standards style of writing pseudo codes.
cannot be compiled or executed and there is no real formatting or syntax rules
Example 1: Suppose you are required to design an algorithm for finding the
average of three numbers, and the sum of the numbers is given. The pseudocode
will be as follows:
Start
Get the sum
Average = sum / 3
Output the average
Stop
DECISION TABLE
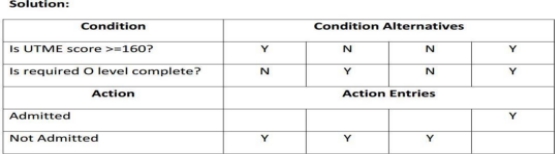
A decision table is a way of representing an
algorithm in a tabular form. It consists of rows and columns, divided into four quadrants as follows:

Conditions: contains a list of all possible conditions pertaining to a problem. Condition Alternatives: contains the condition rules (set of possible values for each condition) of alternatives.
Actions: Contains the action rules, which can be a procedure or operation to be performed.
Action Entries: contains the action rules which specified the action to be performed on the basis of the set of condition alternatives corresponding to that action entry
Example
A student can only be admitted into Gombe State University through UTME with a UTME pass mark of not less than 160 and required O level passes. Draw a decision table for the above case.
Benefits of decision tables
A decision table is generally preferred over flowchart because of the following:
It is easier to draw and modify
For algorithms having complex problem solving logic, a flowchart may take a
number of pages unlike decision table.
COMPUTER THREATS AND SECURITY
To prevent theft of or damage to the hardware
To prevent theft of or damage to the information
To prevent disruption of service
Definition
Computer Security is the protection afforded to computer networks in order to
attain the fundamental objectives of preserving the confidentiality, integrity and availability of system resources, which includes hardware, software, firmware, information or data, and telecommunications.
- Confidentiality of systems and communications. This is a requirement to avoid unauthorized disclosure of systems and communications either intentionally or inadvertently. 2. Integrity of computer networks, data and information. This is a requirement aimed to ascertain that computer networks and their offered services are accurate, complete, consistent, authentic and timely. 2. Availability of computer networks and its offered services. This is a requirement to ensure systems and their offered services are available at accepted levels to legitimate entities.
Threats to computer networks are defined as entities, events or circumstances with the capability to inflict harm or distort normal security operations by exploiting vulnerabilities in systems.
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a program that may disturb the normal working of a computer system. Virus attaches itself to files stored on floppy disks, USBs, email attachments and hard disks.
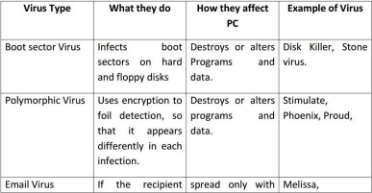

Types of Computer Virus Causes of Computer Virus
The following are the main causes of a Computer Virus.
Infected Flash Drives or Disks
Flash drives and disks are the main cause of spreading viruses.
Email Attachments
Most of the viruses spread through emails. Email attachment is a file that is sent
along with an email. An email may contain an infected file attachment.
Infected / Pornography websites
Thousands of insecure websites can infect computer with viruses. Most of the
websites with pornographic materials are infected, so by visiting these websites
the user’s computer also gets infected by virus.
Networks
Virus can spread if an infected computer is connected to a network.
Pirated Software
An illegal copy of software is called pirated software. Virus can spread if user
installs pirated software that contains a virus.
Protection from Computer Virus
A computer system can be protected from virus by following these precautions.
- The latest and updated version of Anti-Virus and firewall should be installed on
the computer.
- The Anti-Virus software must be upgraded regularly.
- USB drives should be scanned for viruses, and should not be used on infected
computers.
- Junk or unknown emails should not be opened and must be deleted
straightaway
- Unauthorized or pirated software should not be installed on the computer.
- An important way of protection against virus is the use of back up of data.
- Freeware and shareware software from the internet normally contain viruses.
It is important to check the software before using them.
- Your best protection is your common sense. Never click on suspicious links,
never download songs, videos or files from suspicious websites.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written using a Computer Programming Language to perform a specified task by the computer. Computer program instructions are also called program source code and
computer programming is also called program coding.
Compiler
You write your computer program using your favorite programming language and
save it in a text file called the program file. Now let us try to get a little more
detail on how the computer understands a program written by you using a programming language.
Data Types
As its name indicates, a data type represents a type of the data which you can
process using your computer program. It can be numeric, alphanumeric, decimal,
etc.
Variables
Variables are the names you give to computer memory locations which are used
to store values in a computer program. Here are the following three simple steps:
Create variables with appropriate names.
- Store your values in those two variables.
- Retrieve and use the stored values from the variables.
Example1:
{i
nt a;
int b;
}
The above program creates two variables to reserve two memory locations with names a and b. We created these variables using int keyword to specify variable data type which means we want to store integer values in these two variables.Similarly, you can create variables to store long, float, char, or any other data type. Example2:
{i
nt a;
int b;
a = 10;
b = 20;
}
Rules for Constructing Variable Name
- Characters Allowed :
- Underscore(_)
- Capital Letters ( A – Z )
- Small Letters ( a – z )
- Digits ( 0 – 9 )
- Blanks & Commas are not allowed
- No Special Symbols other than underscore(_) are allowed
- First Character should be alphabet or Underscore
- Variable name Should not be Reserved Word